Cellular IoT technology introduces new opportunities for asset tracking and data collection. The technology connects “things” to the internet using the same networks that mobile phones use. As these networks improve and expand across the globe, more and more organizations are adopting this technology. In fact, Market and Research estimates that 4.15 billion people will be connected through cellular IoT by 2024.
What is cellular IoT?
Cellular IoT beacons, just like BLE beacons, make everyday objects ‘smart’ by connecting them to the internet. The technologies are similar; however, their situational capabilities differ. BLE beacons send data to Wi-Fi-enabled or cellular-enabled gateways, which are placed within indoor locations or plugged into vehicles. This makes BLE beacons ideal for indoor applications. Cellular beacons, on the other hand, use the same networks as mobile phones and work wherever there is cell service. They do not require a gateway to transmit data. As a result, they are great for outdoor applications.
There are two main types of cellular IoT: LTE-M and NB-IoT. The US, Netherlands, and Australia have national LTE coverage, which is compatible with LTE-M cellular IoT devices. GSM is the primary cellular network in Africa and Eastern Europe, which is compatible with NB-IoT cellular IoT devices. LTE-M cellular beacons easily interact with the cloud and are the best choice for real-time data transfer. NB-IoT cellular beacons, however, are best at transferring only small amounts of data at a time.
What are its benefits & limitations?
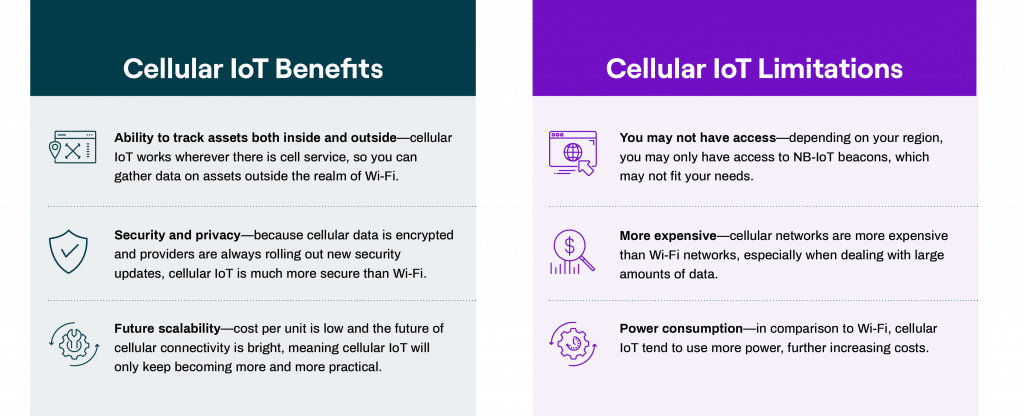
Like any technology, there are pros and cons to implementing this technology into your organization. It is important to consider where cellular IoT can enhance your operations as well as where it may fall short.
How are companies using cellular IoT technology?
Supply Chain Visibility
Many firms use cellular beacons to track high-value goods and other items through the supply chain. Beacons capture real-time location, vibration, movement, and other data. With this information, companies pinpoint asset location, identify potential delays, and confirm proof of delivery. Over time, companies implement advanced analytics modeling to derive additional insight from supply chain data:
- Supply Chain Route Optimization. Evaluate location data on supply chain routes to identify those that offer optimal delivery time.
- Vibration Analysis. Analyze vibration data to identify potential sources of damaged items.
- Root Cause Analysis. Uses location data and employee feedback data to identify process gaps, inefficiencies, and opportunities to improve workflows.
Cold Chain Monitoring
Cellular beacons provide real-time tracking of temperature-controlled products like food, medicine, and chemicals. If temperature or other environmental conditions trend out of compliance, IoT platforms are configured to send a detailed alert. This makes it possible for firms to handle problems in real time.
Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring
Cities use cellular IoT beacons to capture and evaluate outdoor air quality at street-level. This provides city leaders with data and insight to inform policy, map transit routes and more. In addition, companies use a mix of BLE and cellular beacons to create a comprehensive campus air quality map. Together, the beacons monitor particular matter both indoors and outdoors, providing data to enhance employee safety, comply with environmental regulations, and even plan for building maintenance needs.
Optimize your supply chain with Thinaer’s fully intelligent IoT platform.
